- What is a dental abscess?
- Types of dental abscesses
- Symptoms of a dental abscess
- How does a dental abscess form?
- Causes of dental abscess – how to maintain oral health and avoid infection
- How is a periapical abscess diagnosed?
- Dental abscess treatment
- What are the complications of an untreated dental abscess?
- How to prevent dental abscesses
- Conclusion
A dental abscess is one of the most common and at the same time most painful dental conditions. It is an inflammatory process involving the accumulation of pus in the tissues surrounding a tooth. An abscess is typically caused by a bacterial infection that develops due to untreated tooth decay, pulpitis, or periodontal disease. If left undiagnosed and untreated, it may lead to serious complications. In this article, you will learn what a dental abscess is, what its symptoms and causes are, whether it can be cured, and how to prevent it.
What is a dental abscess?
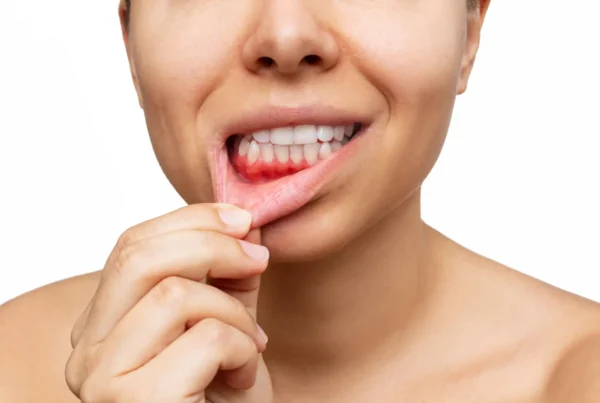
A dental abscess refers to a periapical or periodontal abscess—types of inflammation characterized by the buildup of purulent fluid in tissues around the tooth, most commonly due to bacterial infection. When the abscess fills with pus, symptoms such as pressure and pain may arise, including the sensation of the tooth being “pushed out” of its socket. Pus, which consists of dead cells, bacteria, and their metabolic byproducts, collects in a confined space, causing severe pain and swelling. A dental abscess is a serious condition and should never be ignored.
Types of dental abscesses
- Periapical abscess – forms at the root tip of the tooth, usually due to untreated pulpitis leading to pulp necrosis
- Periodontal abscess – develops in the supporting tissues of the tooth, often associated with advanced gum disease
- Gingival abscess – confined to the gum tissue, typically caused by trauma or localized infection
- Submucosal abscess – a collection of fluid beneath the oral mucosa, often related to inflammation
- Subperiosteal abscess – accumulation of pus between bone and periosteum, commonly due to trauma or infection
Each type of dental abscess can have serious health consequences if not treated appropriately. Fortunately, modern dentistry offers effective prevention and treatment strategies to protect oral health.
Symptoms of a dental abscess
A dental abscess presents with a range of characteristic symptoms, which may vary in intensity depending on the progression of the infection.
Common symptoms include:
- Severe, throbbing toothache – worsens with chewing, biting, or pressure
- Swelling of gums and face – localized swelling that can spread across the face in severe cases
- Red, inflamed gums – especially around the affected tooth
- Pus discharge – pus may drain through the gum or a fistula, often bringing temporary pain relief
- Bad breath (halitosis) – due to bacterial overgrowth and accumulation of waste products
- Darkened tooth color – especially in cases of pulp necrosis
Systemic symptoms may include:
- Fever, chills, and general malaise
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the jaw or neck area
- Trismus (difficulty opening the mouth)
- Lowered immune cell count
- Noticeable cosmetic changes to the tooth
If these symptoms appear, immediate dental consultation is crucial. Untreated abscesses may spread to surrounding tissues and cause serious complications, including tooth loss.
Read more: Brown stains on teeth
How does a dental abscess form?
A dental abscess forms due to bacterial infection that spreads from the tooth chamber into surrounding tissues, triggering inflammation and pus accumulation in the alveolar bone. The development of an abscess depends on the extent of bacterial infection and structural damage that allows microorganisms to penetrate the pulp and adjacent areas.
Causes of dental abscess – how to maintain oral health and avoid infection
- Untreated tooth decay – bacteria from advanced cavities can reach the pulp, causing inflammation and necrosis
- Pulpitis – untreated pulp inflammation leads to tissue death and infection at the tooth root
- Periodontal disease – deep gum pockets harbor bacteria that may cause abscess formation
- Dental trauma – fractures, cracks, or gum injuries can facilitate bacterial entry
- Post-treatment complications – improperly performed root canal treatments or tooth extractions may result in infections
- Weakened immunity – patients with chronic conditions (e.g., diabetes) are more susceptible to spontaneous oral infections
How is a periapical abscess diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on a thorough clinical exam and additional diagnostic tests.
- Medical interview – the dentist asks about symptoms, duration of pain, and prior issues with the affected tooth
- Clinical examination – assesses gum condition, swelling, redness, and possible pus discharge
- Imaging – dental X-rays are crucial for evaluating the tooth’s interior, bone integrity, and adjacent structures. In complex cases, cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) may be necessary
- Laboratory tests – in some cases, pus samples are taken for microbiological analysis to determine the most effective antibiotic therapy
Dental abscess treatment
Treatment depends on the location, severity of the abscess, and the patient’s overall condition. Key treatment methods include:
Elimination of the infection source:
- Endodontic (root canal) therapy – removes necrotic pulp and thoroughly cleans the root canals
- Deep cleaning of periodontal pockets – necessary for periodontal abscesses
Abscess drainage:
The dentist may incise the abscess to release pus and reduce pressure.
Pharmacotherapy:
- Antibiotics – such as amoxicillin or clindamycin to combat bacterial infection
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs – e.g., ibuprofen to relieve symptoms
Tooth extraction:
In cases where the tooth is beyond repair, extraction may be required.
What are the complications of an untreated dental abscess?
A dental abscess, especially when linked to the pulp chamber, can cause serious issues if not treated:
- Spread of infection to surrounding tissues, including jawbone
- Formation of fistulas that damage nearby teeth
- Cellulitis – diffuse inflammation of soft tissues
- Life-threatening conditions like sepsis or endocarditis
How to prevent dental abscesses
Preventive strategies include maintaining daily oral hygiene and regular dental care:
- Daily brushing with fluoride toothpaste and use of dental floss
- Home remedies such as cold compresses and mouth rinses
- Routine dental check-ups
- Prompt treatment of cavities and other dental issues
- Healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamins
Conclusion
A dental abscess is a serious infection that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. It causes intense pain due to inflammation and pus accumulation near the root tip. This condition is associated with general malaise, swelling, and various unpleasant symptoms that can lead to dangerous complications and pose a risk to overall health. Avoiding dental neglect and maintaining regular oral hygiene is crucial. Routine dental visits help prevent infection and ensure a healthy smile for years to come.





