- Causes of brown stains on teeth – why do dark spots appear?
- Home remedies for removing tooth stains – are they effective?
- Can over-the-counter products remove brown stains?
- Professional solutions for removing tooth discoloration
- How to prevent brown stains on teeth?
- Summary – what causes brown spots on teeth and how to remove them?
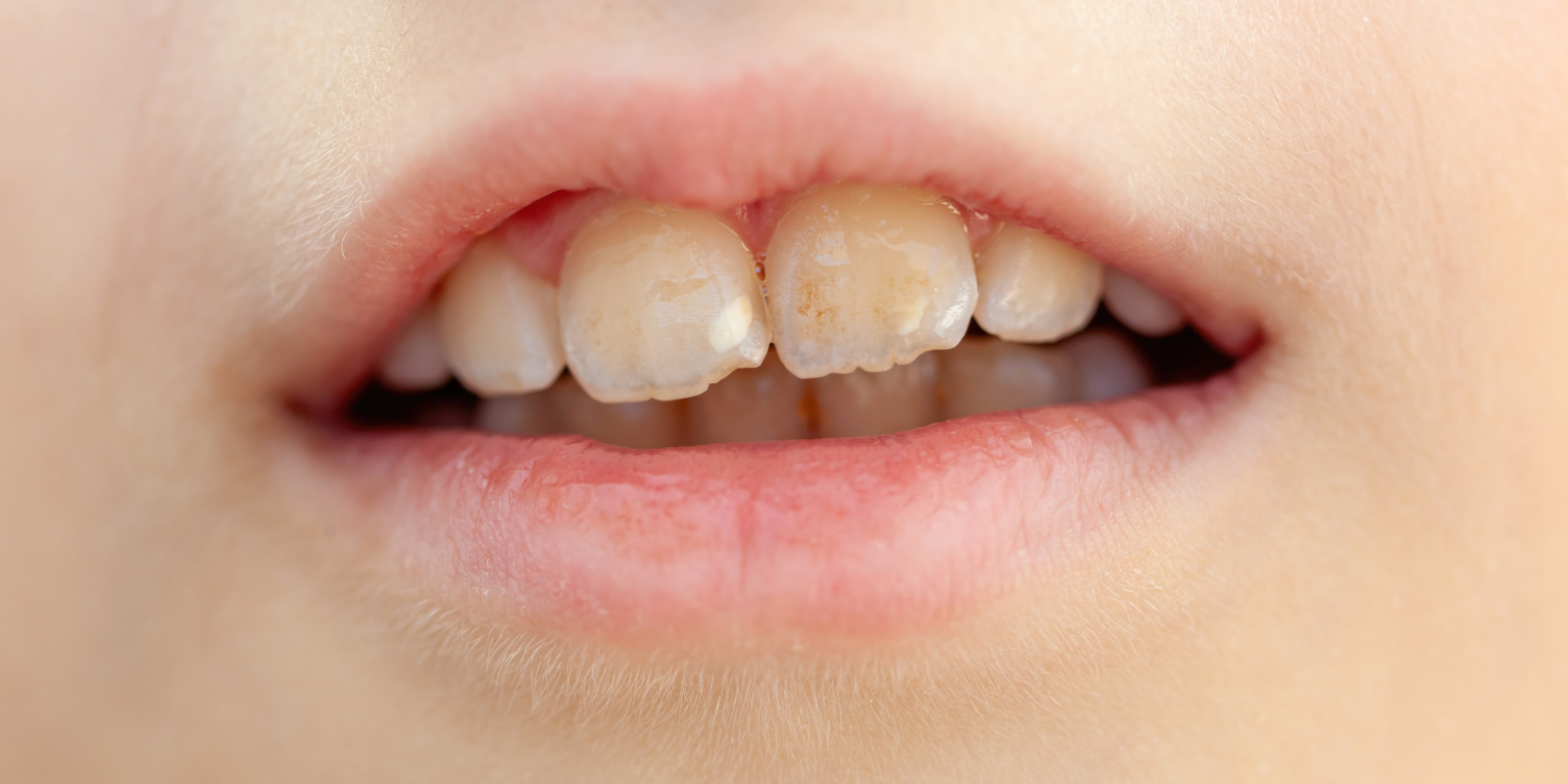 A beautiful, healthy smile is something many people strive for, but tooth discoloration can make it more difficult to achieve. Brown stains are a common aesthetic concern that can affect our self-esteem and how others perceive us. Not only brown, but also dark, white, and gray spots on the teeth can affect the appearance of the smile and lower our confidence. The appearance of our teeth plays a significant role in shaping our image, and discoloration is a widespread issue that affects people of all ages. Let’s explore where these stains come from and how to effectively deal with them.
A beautiful, healthy smile is something many people strive for, but tooth discoloration can make it more difficult to achieve. Brown stains are a common aesthetic concern that can affect our self-esteem and how others perceive us. Not only brown, but also dark, white, and gray spots on the teeth can affect the appearance of the smile and lower our confidence. The appearance of our teeth plays a significant role in shaping our image, and discoloration is a widespread issue that affects people of all ages. Let’s explore where these stains come from and how to effectively deal with them.
Causes of brown stains on teeth – why do dark spots appear?
Wondering what causes brown discoloration on your teeth? It can affect both permanent and baby teeth and stem from various sources. Brown discoloration may be a purely cosmetic issue or a sign of underlying oral health problems. Not just dark, but also white spots may indicate enamel demineralization, which weakens tooth structure. The causes of discoloration are diverse, ranging from external factors like diet to internal bodily processes. Understanding their origin is key to effective treatment.
Dietary habits and lifestyle
One of the most common causes of brown stains is diet and lifestyle. Pigmented food and drinks can cause brown or black discoloration on the enamel’s surface. An inadequate diet may also lead to white spots, an early sign of weakened enamel.
Highly pigmented food and drinks, such as coffee, tea, and red wine, can stain the enamel over time. Sugary and acidic carbonated beverages may not only stain but also erode enamel, increasing the risk of cavities. Smoking and chewing betel nuts lead to persistent, hard-to-remove stains due to tar and nicotine.
Poor oral hygiene
Insufficient hygiene promotes plaque buildup, and over time, brown marks may appear along the gum line and between teeth. Plaque, a bacterial film, can mineralize into tartar, which usually has a brown or yellow tint and can only be removed by a professional cleaning. Left untreated, tartar increases the risk of decay and cavities. Low-quality or irregular use of dental products, including toothpaste, rinses, and floss, also contributes to discoloration.
Medical factors
Fluorosis caused by excessive fluoride intake during tooth development can result in white or brown stains. The use of certain medications, especially tetracycline antibiotics taken during pregnancy or childhood, can lead to permanent tooth discoloration. Other drugs like iron supplements may also darken teeth. Genetic or acquired enamel and dentin disorders such as amelogenesis imperfecta or dentinogenesis imperfecta may cause deep, persistent stains. Internal discoloration may be linked to pulp necrosis or chronic inflammation.
Age and genetics
As we age, enamel becomes thinner and more translucent, exposing the darker dentin beneath. Genetics also play a role, influencing enamel thickness, natural color, and susceptibility to stains. People with thinner enamel are more likely to show brownish tones as dentin is more visible.
Environmental factors
External conditions may influence tooth color. For example, children may develop discoloration from high fluoride levels in drinking water, leading to visible changes in enamel. Occupational exposure to industrial chemicals may also cause staining.
Bruxism
Habitual teeth grinding or clenching, known as bruxism, wears down the enamel. The weakened surface is more prone to both surface and deep staining.
READ MORE: Dental hygiene treatment
Home remedies for removing tooth stains – are they effective?
Many people seek natural or home solutions to prevent or reduce discoloration. Proper oral hygiene is the first and most important step. Brushing at least twice a day with a whitening toothpaste helps remove buildup. Flossing eliminates food and bacteria between teeth, while mouthwash helps clean areas around orthodontic appliances and reduces plaque.
Natural whitening methods – do they really work?
Baking soda mixed with water forms a paste that may help remove surface stains through mild abrasion. Coconut oil pulling, which involves swishing oil in the mouth for several minutes, is thought to remove toxins and reduce plaque. Fruit acids in strawberries or lemons may offer mild whitening effects, but overuse may weaken the enamel and should be approached with caution.
Can over-the-counter products remove brown stains?
Whitening strips, gels, and trays may help with superficial stains. These products are easy to use and provide visible results in a short period of time. However, they must be used as directed to avoid side effects such as sensitivity or gum irritation. Their effectiveness depends on the type and depth of the discoloration.
Home whitening methods may work for mild cases, especially when used consistently and carefully. Good habits and regular hygiene are the foundation of a healthy, white smile.
Professional solutions for removing tooth discoloration
In-office treatments deliver faster, long-lasting results, especially for persistent stains or internal discoloration. Scaling removes tartar, often brown or yellow in color, and can be followed by air polishing, which uses water and powder to remove surface stains. These treatments are quick, painless, and immediately improve appearance.
Professional whitening, using hydrogen peroxide, penetrates enamel to lift stains. Laser whitening involves applying a bleaching gel activated by laser light, while LED whitening uses light to enhance whitening agents. Both are safe and effective, though temporary sensitivity may occur.
For severe discoloration, porcelain or composite veneers may be recommended. These thin shells cover the tooth surface and restore color and shape. In cases of more extensive damage or discoloration, dental crowns may be necessary to fully restore the tooth.
Professional treatments are ideal for those seeking durable results and willing to invest in their smile. A dental consultation is essential to assess tooth condition and select the best method. Proper hygiene and follow-up care help maintain results and prevent recurrence.
How to prevent brown stains on teeth?
Prevention involves combining good oral hygiene, healthy habits, and a conscious approach to diet and lifestyle. Regular professional whitening and using the right products are key to keeping stains away. Since most stains are linked to daily routines, changing habits is the best way to protect your smile.
Brush your teeth twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste and use a sonic toothbrush for optimal results. Floss daily to clean between teeth, and use antibacterial mouthwash to limit plaque buildup. Visit your dentist every six months for check-ups and cleanings like scaling and polishing, which remove buildup and stains.
Limit staining foods and drinks such as coffee, tea, wine, beets, and berries. Use a straw when drinking colored beverages to reduce contact with enamel. Rinse your mouth with water after consuming staining foods. Eat crunchy fruits and vegetables like carrots and apples to naturally clean your teeth.
Quit smoking and avoid chewing tobacco, as both cause stubborn stains. Reduce sugar intake to limit plaque formation. Stay hydrated to support saliva production, and consume foods rich in calcium and vitamins, such as dairy, leafy greens, and nuts.
Use gentle whitening toothpaste and avoid overusing whitening products, which may weaken enamel. Follow your dentist’s aftercare instructions after whitening procedures.
Educate yourself about oral health to better understand what causes discoloration. If in doubt, speak with your dentist to identify the best care products and strategies.
Summary – what causes brown spots on teeth and how to remove them?
Brown stains on teeth may result from lifestyle habits, poor hygiene, medical conditions, or genetics. While some stains are harmless, others may signal serious oral health issues. Frequent discoloration should be evaluated by a dentist to rule out systemic conditions. Understanding the cause is essential for choosing the right solution. Some stains can be removed with home care or professional cleanings, while others require advanced treatment. Prevention through healthy routines, proper hygiene, and regular dental visits ensures a bright, confident smile for years to come.





